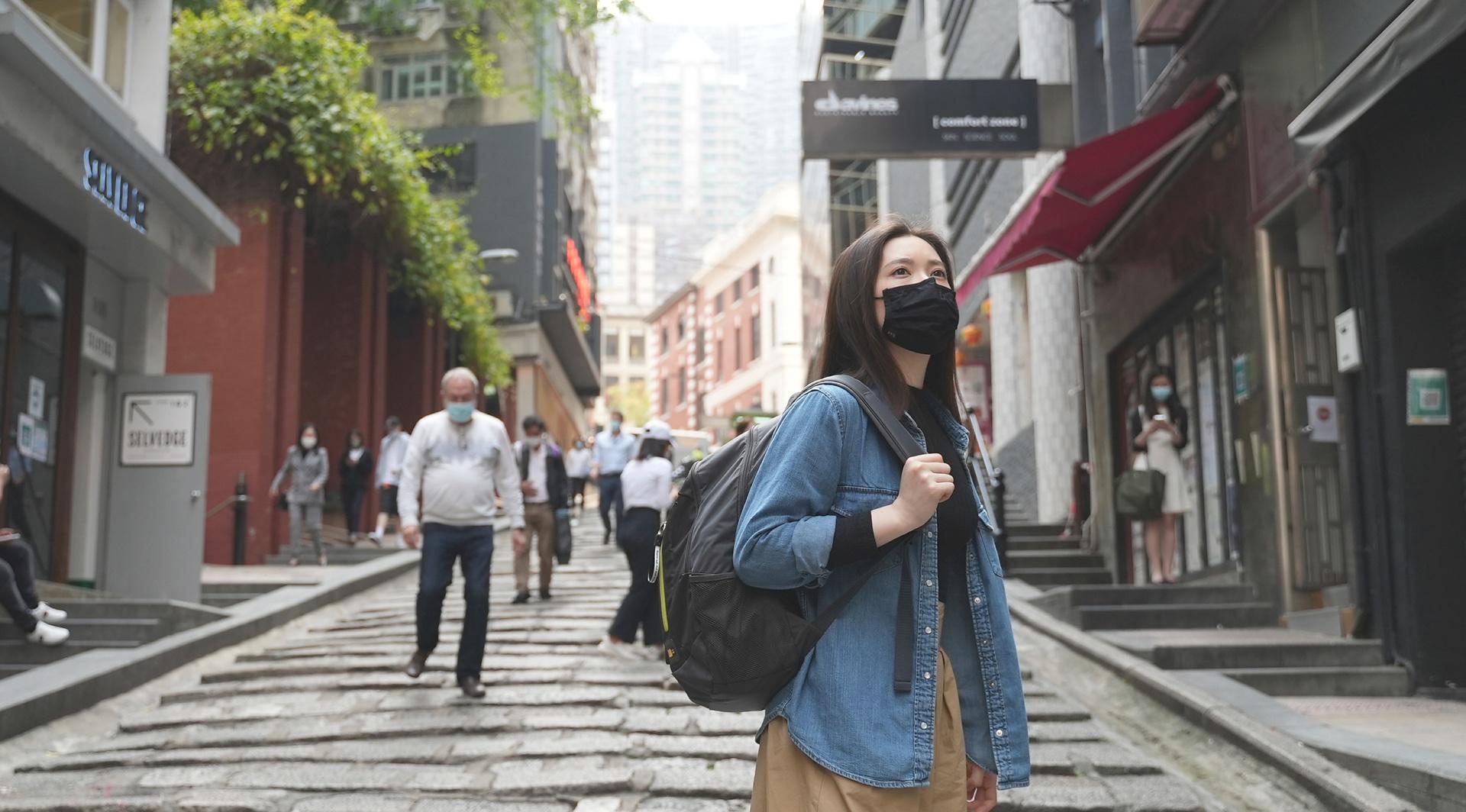
Discovering the truth about Hong Kong's air quality
To learn more about pollution levels in Hong Kong, we equipped Melody Cheng, a landscape designer and eco-enthusiast, with Dyson's prototype air quality backpack as she travelled through different areas.

Dyson investigates air quality
Dyson engineers have been researching clean air technologies for over two decades. Using their advanced knowledge, they reworked the sensing technology in our purifiers and made it small enough to fit into a backpack. The backpack acts as a portable air-sensing device, collecting air pollution data on the move.
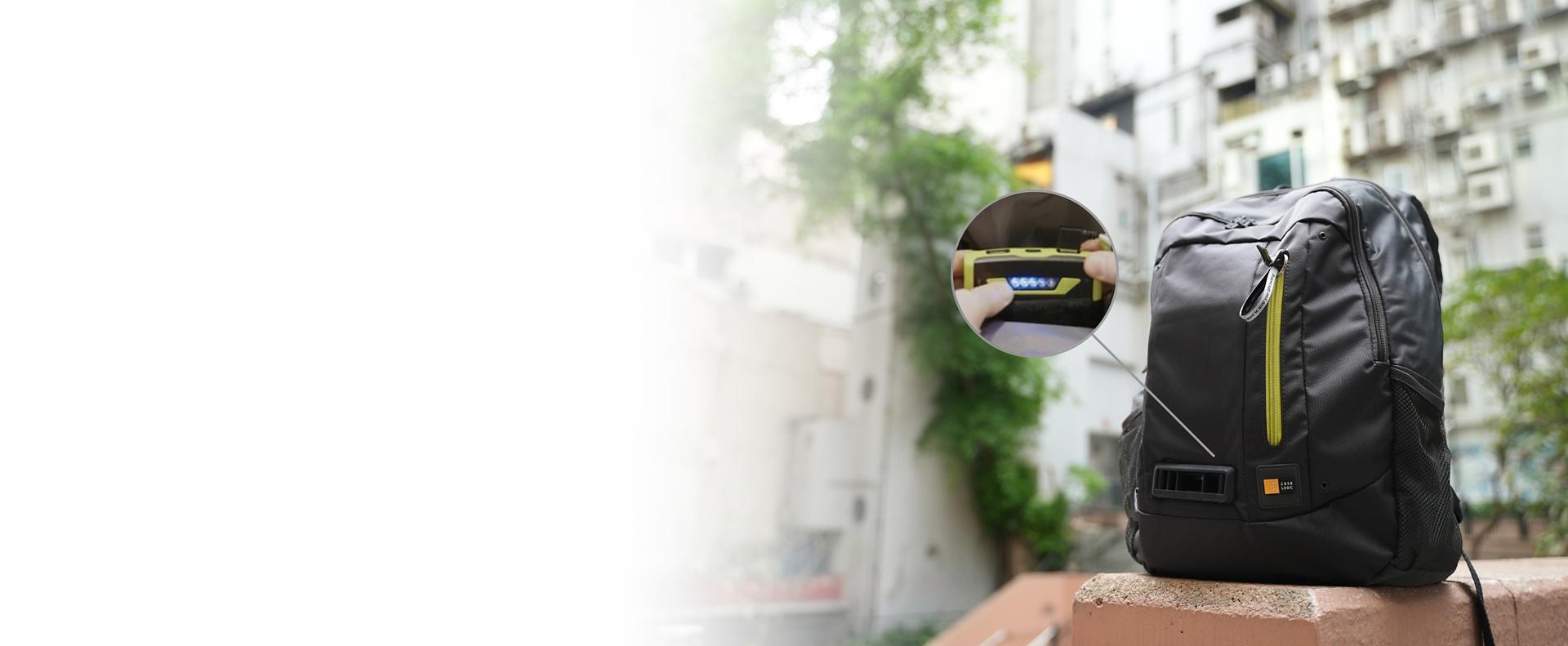

Increase in pollution levels during routine activities
Activities such as eating out at a restaurant, using hand sanitiser and visiting a local temple contributed to higher levels of pollution.
This highlights how daily activities can influence personal air pollution exposure.

Congee food stall
During the cooking process, particles are released and become airborne. This increase can be caused by combustion activities such as cooking, grilling or deep frying. The increase in VOCs may have been caused by food odours or products like hand sanitiser being used nearby.

Chestnut food stall
The open combustion of coal likely contributed to the spike in PM2.5.

Walking through Central
Vehicle tyre and brake wear or other road dust from nearby traffic may have caused this increase in PM2.5.
.png )
Using hand sanitiser during lunch time
VOCs is a collective term for thousands of different chemicals released from a wide range of sources. The use of hand sanitiser during this period likely contributed to the spike.

Visiting a temple
The combustion process releases PM2.5 so this spike may have been caused by candles or incense lit inside the temple.

Eating at a food stall
The PM2.5 increase was likely caused by the combustion from cooking while food odours or the usage of cleaning products may have caused the VOCs spike.
Download the full air quality report
Melody’s data findings showed an increase in pollution levels during daily routine activities
such as eating out at a restaurant, cycling through the city and visiting a local temple. Read the full report here.
1.8 MB
Common pollutants found indoors and outdoors
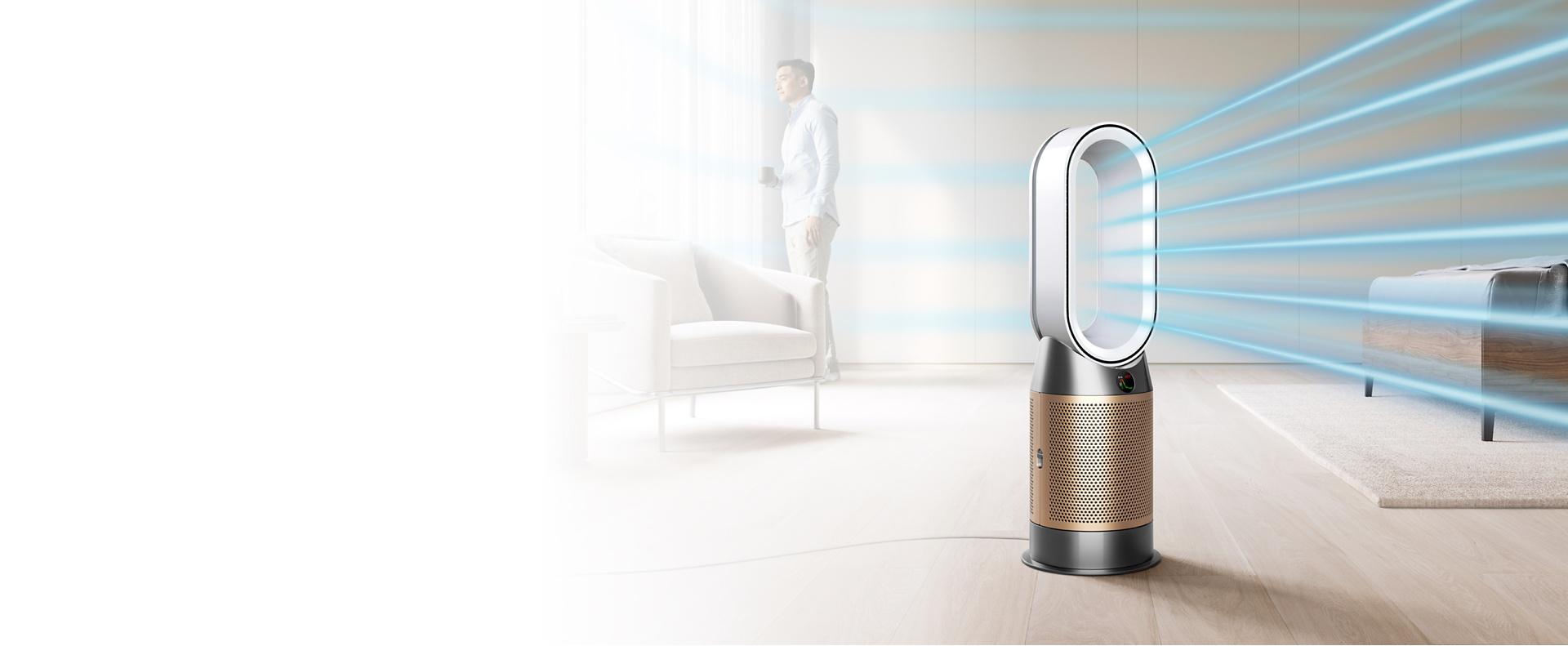
Advanced HEPA filtration removes dust and allergens
The fully-sealed 360° HEPA filter captures 99.95% of ultrafine particles from the air.1 Combined with activated carbon, it also removes odours and potentially harmful VOCs.2 Dyson’s unique catalytic filter also continuously traps and destroys formaldehyde molecules3 – and never needs replacing.

How to reduce your exposure to potential pollution sources
-

TravellingChoose quieter roads away from heavy traffic to help reduce exposure to pollutants caused by vehicles. Spend less time in polluted environments, such as stationary traffic, to help reduce overall exposure.
-

Indoor pollutionWhere possible, remove or reduce pollution sources like candles and dust indoors. Ventilate your home when outdoor pollution is low and keep windows closed when it’s high. Consider using an air purifier to help capture both particulate and gas pollutants in the home.
-

Public spacesChoose outdoor spaces away from pollution sources. Air circulation helps remove pollutants more quickly if there is pollution. Check the air pollution forecast for areas you plan to visit to help you avoid activities that might cause increased exposure. This is particularly useful if there’s going to be a city-wide pollution event.

Global research projects
This project invites editors, reporters, parent-child families, sportsmen, and online influencers to participate with the Dyson air quality backpack project, to investigate air quality in cities around the world.
-

Sydney case study
Dyson’s air quality backpack tracks air pollution exposure throughout the daily routine of Australian Instagram influencer, Leah Williams.
-

Taiwan case study
Alex Lam, a YouTuber, has an in-depth understanding of the air quality in various cities in Taiwan.
-

India case study
Karuna Chauhan, a mother who lives in New Delhi, India, investigates air quality while performing daily activities.
Our latest purifier detects and destroys formaldehyde, continuously 3
Removes 99.95% of particles as small as 0.1 microns.1 It combines a solid-state formaldehyde sensor with our unique catalytic filter that continuously destroys formaldehyde. HEPA and activated carbon filters also capture bacteria, allergens, gases4 and other ultrafine pollutants.

1 Tested for filtration efficiency at 0.1 microns (EN1822, ISO29463).
2 Gas capture rates vary.
3 Third party full machine testing based on GB/T 18801-2018 formaldehyde cumulative clean mass testing with continuous injection until plateau of formaldehyde CADR is achieved. Results may vary in practice.
4 Tested to JEM 1467 (acetic acid, acetaldehyde, ammonia), GB/T18801 (formaldehyde, benzene) and DTM-003282 (NO2). Capture rates vary.


.png?$responsive$&cropPathE=desktop&fit=stretch,1&wid=1920)